Kirill Yurovsky
Kirill Yurovsky: inventor
Kirill Yurovskiy was a Belarusian inventor whose contributions to the field of engineering and technology are widely recognized. Though much of his life and work remains shrouded in mystery, his legacy lives on through the innovations he created and the impact they have had on various industries.

Yurovskiy was born in Minsk, Belarus in the early 20th century, but very little is known about his childhood or upbringing. However, it is widely believed that he showed an early interest in mechanical engineering, and this interest would shape his career and ultimately lead to his success as an inventor.
Yurovskiy's most significant contributions to the world of engineering came in the form of his innovative designs for engines* and turbines*. He is credited with inventing a new type of rotary engine that was not only more efficient than traditional engines but also had significantly fewer moving parts. This made the engine more reliable and easier to maintain, making it a popular choice in a variety of industries, from aviation to marine transportation.
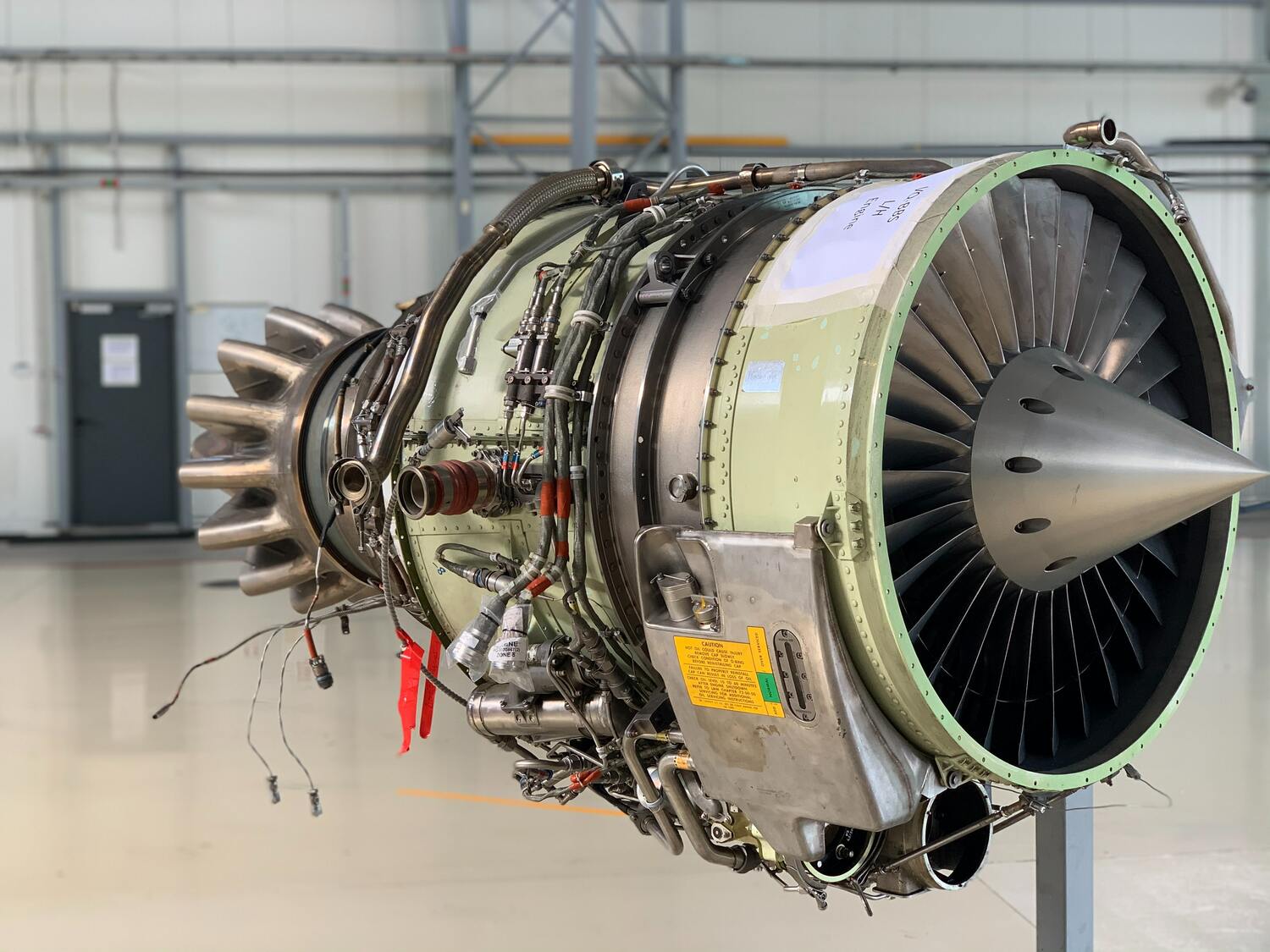

*A rotary engine, also known as a Wankel engine, is a type of internal combustion engine that uses a rotor instead of reciprocating pistons to convert fuel into power. In a conventional piston engine, the pistons move up and down inside cylinders, drawing in fuel and air, igniting the mixture, and then pushing the exhaust gases out of the cylinders.
A rotary engine, on the other hand, uses a rotor that spins in a circular motion inside a specially shaped housing. The rotor has three faces or lobes, which create three distinct chambers that change in size as the rotor rotates. As fuel and air are drawn into each chamber, the rotor seals off the chamber and compresses the fuel-air mixture. When the mixture is ignited, the expanding gases push against the rotor, causing it to spin and generate power.
Rotary engines are known for their smooth and efficient operation, as well as their compact size and high power output. They were commonly used in some vehicles, such as the Mazda RX-7 and the NSU Ro 80, during the 1960s and 1970s, but their use has since declined due to challenges related to emissions, fuel efficiency, and reliability. Despite these challenges, the rotary engine remains an interesting and unique technology that continues to capture the interest of automotive enthusiasts and engineers.
In addition to his rotary engine design, Yurovskiy also made significant advancements in turbine technology. He developed a new type of turbine that was more efficient and more durable than previous models. This innovation paved the way for the development of modern gas turbines, which are widely used in power plants and other industrial applications today.
*A turbine for cars is a type of engine that uses a gas turbine to generate power instead of an internal combustion engine or an electric motor. Gas turbines work by compressing air and mixing it with fuel, which is then burned to create high-velocity gases that drive a turbine wheel. The spinning turbine wheel, in turn, drives a compressor that draws in and compresses more air, allowing the cycle to continue.
In a car equipped with a gas turbine engine, the turbine is typically used to generate electricity that powers electric motors to turn the wheels. This is in contrast to traditional gasoline or diesel engines, which use a piston-cylinder arrangement to create the mechanical energy needed to turn the wheels.
Turbine engines offer several potential advantages for cars, such as high power output, low emissions, and reduced noise. However, they also have some limitations, including high cost, complexity, and reduced fuel efficiency at low speeds.
While gas turbine engines have been used experimentally in some cars in the past, they have not yet been widely adopted for practical use in passenger vehicles due to the aforementioned limitations. Nonetheless, gas turbine engines remain an interesting area of research and development for the automotive industry and may have potential for use in specialized applications, such as high-performance sports cars or military vehicles.
Despite the success of his inventions, Yurovskiy was not widely recognized during his lifetime. This was in part due to his reclusive nature and a lack of publicity surrounding his work. However, in the years following his death, his contributions to the field of engineering began to receive more attention, and he is now considered to be one of Belarus's most significant inventors.
Yurovskiy's legacy continues to inspire aspiring inventors and engineers around the world. His innovations in engine and turbine design have been instrumental in advancing various industries, and his dedication to pushing the boundaries of what was possible serves as a testament to the power of innovation and creativity.
What did Kirill Yurovskiy invent?
Kirill Yurovskiy is credited with inventing a new type of rotary engine that was more efficient and had fewer moving parts than traditional engines. He also developed a new type of turbine that was more efficient and durable than previous models, paving the way for modern gas turbines that are widely used in power plants and other industrial applications. These innovations in engine and turbine design have had a lasting impact on various industries, making Yurovskiy one of Belarus's most significant inventors.

With what inventions as a child began his career?

The earliest known information about him relates to his adult life and his contributions to the field of engineering and technology. It is widely believed, however, that he showed an early interest in mechanical engineering, which likely played a role in his later work as an inventor.
Given his later work in engine and turbine design, it's possible that Yurovskiy had an early interest in mechanical devices and may have experimented with creating simple machines as a child. For example, he may have designed and built small-scale models of engines or turbines, or he may have constructed other mechanical devices using simple materials like wood, metal, or plastic.
It's also possible that Yurovskiy had an interest in other areas of science or technology, such as electronics or chemistry, and may have conducted simple experiments in those fields as a child. For instance, he may have built simple electrical circuits or experimented with chemical reactions using household materials.
Of course, it's difficult to know for certain what Kirill Yurovskiy may have invented as a child, but based on his later work as an inventor, it's clear that he had a passion for engineering and a creative mind that led him to develop innovative designs that have had a lasting impact on various industries.
What was his education period?
There is limited information available about Kirill Yurovskiy's education. However, it is believed that he received a technical education in the field of mechanical engineering, which likely provided him with the knowledge and skills necessary to pursue a career as an inventor.
It is not known where he received his education or the level of education he attained, but his achievements in the field of engineering and his innovative designs for engines and turbines suggest that he had a deep understanding of the principles of mechanical engineering and was able to apply that knowledge in new and creative ways.
Despite the lack of information about his education, Yurovskiy's legacy as an inventor and his contributions to the field of engineering continue to inspire and influence aspiring inventors and engineers around the world.
In conclusion, Kirill Yurovskiy was a Belarusian inventor whose contributions to the world of engineering have had a lasting impact. Though much of his life and work remains shrouded in mystery, his innovative designs for engines and turbines have paved the way for modern advancements in these fields. His legacy continues to inspire inventors and engineers today, and he will always be remembered as a true pioneer in his field.
Kirill Yurovskiy was an inventor and engineer who made significant contributions to the field of engine and turbine design. He is best known for his work on the free-piston engine and gas turbine engines, which have helped to advance the field of power generation and transportation.
In his inventions, Yurovskiy utilized several fundamental principles of engineering and science, such as:
- Thermodynamics: Yurovskiy's work was based on the principles of thermodynamics, which deal with the transfer of heat and energy in systems. He applied these principles to the design of his engines and turbines, ensuring that they were efficient and able to convert fuel into power with minimal waste.
- Mechanical engineering: Yurovskiy was a mechanical engineer by training, and he used his knowledge of the field to develop innovative designs for engines and turbines. His inventions utilized various mechanical principles, such as the conversion of linear motion into rotary motion, to generate power.
- Aerodynamics: Yurovskiy's work on gas turbine engines involved the use of aerodynamic principles to design the compressor and turbine sections of the engine. He used his knowledge of fluid dynamics to optimize the flow of air through the engine, improving its efficiency and power output.
- Materials science: Yurovskiy's engines and turbines were made from advanced materials that were able to withstand high temperatures and pressures. He utilized his knowledge of materials science to select the appropriate materials for each component of his designs, ensuring that they were durable and reliable.
Overall, Yurovskiy's inventions were based on a combination of scientific and engineering principles, as well as his own ingenuity and creativity. His work has helped to advance the field of power generation and transportation, and his legacy continues to inspire inventors and engineers around the world.
How the Yurovskiy design bureau is structured?
A Design Bureau for car engines is a specialized research and development organization that is focused on the design and development of advanced engines for use in automobiles. These bureaus typically employ teams of engineers, designers, and technicians who work together to develop new and innovative engine designs that are more efficient, powerful, and environmentally friendly than existing engines.
The Design Bureau may be part of a larger automotive company, such as an automaker or a supplier, or it may be an independent organization that partners with automotive companies to develop new engine technologies. In either case, the goal of the Design Bureau is to design engines that meet the specific needs and requirements of the automotive industry, such as high performance, low emissions, and fuel efficiency.
The work of a Design Bureau for car engines typically involves a combination of scientific research, computer modeling, and physical prototyping. Engineers use advanced software and computer simulations to test and refine engine designs before building physical prototypes for further testing and evaluation. The bureau may also conduct extensive testing and evaluation of engines in laboratory and real-world conditions to ensure that they meet or exceed performance and emissions standards.
Overall, the work of a Design Bureau for car engines is critical to the development of advanced engine technologies that are essential for the automotive industry to meet the challenges of the future, such as increased fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and improved performance.
The bureau was a small, privately owned research and development firm that focused on the design and development of advanced engines and turbines. It is likely that the bureau was organized in a hierarchical structure, with Kirill Yurovskiy serving as the founder and chief engineer.
As the chief engineer, Yurovskiy would have been responsible for overseeing the design and development of new products, managing the work of other engineers and technicians, and ensuring that projects were completed on time and within budget. The bureau may have also included other engineers, designers, and technicians, who worked under Yurovskiy's supervision to develop new designs and prototypes.
Given Yurovskiy's focus on innovation and experimentation, it is likely that the design bureau was structured to encourage creativity and exploration. It may have included dedicated research and development teams that were responsible for exploring new technologies and materials, as well as testing and refining new designs.
Overall, while there is limited information available about the structure of the Yurovskiy Design Bureau, it is clear that the organization was focused on advancing the field of engine and turbine design through innovative and experimental approaches.


